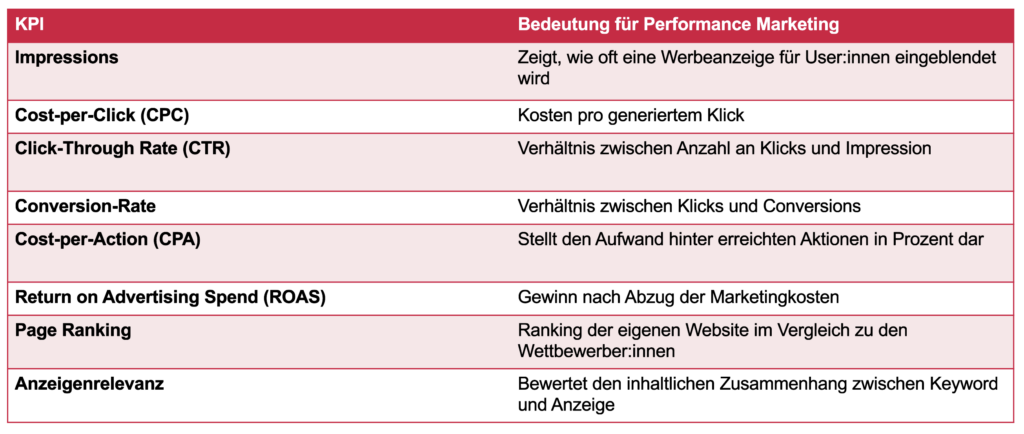
In order to check if your campaigns are successful, you need to have reliable key figures. Various key performance indicators (KPIs) are available to you for performance marketing. They help you to evaluate your Using the marketing budget correctly and support you with Optimization of your performance marketing campaigns.

Click-through rate (CTR)
The click-through rate (CTR) shows how often your ad was clicked on after a playout. It measures the ratio between the number of clicks and the number of impressions. Impressions are the key figure that indicates how often an ad is displayed to users.
Click-through rate (CTR) in percent = (sum of all clicks / sum of all impressions) x 100
The higher the CTR, the more appealing and relevant the ad is to your target audience. However, users may not find the content they want on your website and may not take the action you want. Therefore, you should always also consider the Conversion rate be included in the consideration.
Cost Per Click (CPC)
The CPC is used to find out how high the cost of a click per ad is. Another term for this important key figure in performance marketing is Pay per click (PPC). It is calculated like this:
Cost per click in euros (CPC) = sum of all advertising costs in euros / sum of all clicks
The CPC arises from clicks of all types, whether on Text ads, videos or banners. Often, advertising networks like Google or social media platforms like Facebook work with the CPC for billing.
A click can cost a few cents or double-digit euros. Different factors are taken into account when setting prices:
- Landing page qualityThe more valuable the page is for the user, the lower the CPC.
- Type of advertising mediumVisual advertising media (banners) sometimes have higher click prices than text ads.
- Number of auction participantsnden: Competitors who also participate in the auction for the playout of their ad.
- IndustryIn the finance and consulting industry, for example, the click prices are significantly higher than in other industries because a higher turnover is expected. Thus, auction participants are willing to bid more for the click.
- RelevanceHow relevant is the advertisement for potential customers or clients?
- CTR: What is the expected click-through rate for the ad?
The CPC helps to keep track of the advertising budget. With an analysis tool such as the Google Keyword Planner you can find out how big the competition is and how much the clicks cost on average.
The CPC can also be used to calculate the ROI.
The problem with this metric is that the competition can engage in click manipulation to drive up costs. A click does not always lead to a purchase. And site operators also have to pay for accidental clicks.
Conversion rate
In performance marketing, the term conversion refers to a previously defined, successfully completed action. Advertisers freely determine the content of the action. For example, it can be a download or a visit to a certain subpage.

The conversion rate shows the relationship between clicks and conversions. It therefore reflects the success of whether a click on an ad has actually led to the desired action on the website or in the online store. This performance marketing KPI is calculated as follows:
Conversion rate in percent = (sum of all conversions / sum of all clicks) x 100
Cost Per View (CPV)
CPV is another of the most important performance marketing KPIs. It is used to determine the cost of an advertising measure per view contact. This is how it is calculated:
Cost per view in euros (CPV) = sum of all advertising costs in euros / sum of all active views
CPV is mainly used for video ads. It is counted when users click on a video ad. Video Ad click Play, Skip, or Expand. If a video is viewed for 30 seconds or longer, a call is also recorded. Depending on the network and topic, a video view costs between ten cents and one euro, provided that a view is recorded.
As an advertiser, you have the option to set the click price and thus retain full control over the budget. The disadvantage here is the fact that advertising videos are always run through completely without being noticed. Pop-ups with videos start automatically and are often not even noticed. They cause costs, but do not contribute to the advertising success.
Cost Per Action (CPA)
Cost per action (CPA) is one of the most important performance marketing KPIs. The CPA shows how high the Costs of a marketing measure for a performed action are.
The CPA can be calculated as follows:
Cost per action in Euro = Sum of all advertising costs in euros / sum of all generated actions
With CPA, you can compare campaign successes with each other. It helps to develop bidding strategies and to optimize the advertising platform. However, there are also disadvantages: The key figure is distorted if, for example, customers cancel or return an order. In such a case, the CPA would have to be corrected manually to avoid drawing false conclusions from the results.
Cost Per Order (CPO)
Another important performance marketing indicator is the CPO. It is used to determine how high the costs of an advertising measure are for an order placed. The CPO is calculated as follows:
Cost per order in euros (CPO) = Sum of all advertising costs in euros / Sum of all orders
Advertising costs include all costs incurred in the run-up to an order. They include both the costs for the advertising platform and the other costs of initiating the order.

With CPO, the effectiveness of a marketing campaign can be put in relation to the budget used. In this way, campaigns can be compared with each other. In affiliate marketing, the CPO is used as a billing model. Commission costs are due for each sale. The CPO can be used to determine the percentage of a sale that goes to the affiliate partner.
Cost Per Lead (CPL)
One of the most commonly used performance marketing KPIs is the CPL. It shows how high the advertising costs are for a lead and is calculated as follows:
Cost per lead in euros (CPL) = sum of all advertising costs in euros / sum of all leads
A lead is the contact data that a user leaves behind on a homepage by registering in a contact form or subscribing to a newsletter. The CPL is used as an important key figure everywhere where it is not primarily a matter of sales, but of obtaining contact data. It is also suitable, for example, as a key figure for products that require intensive consultation and/or are high-priced. It can be used to compare the profitability of different advertising campaigns.
One disadvantage of the CPL is that a lead does not yet represent a sales promise. Poor quality leads are also included in the CPL. In addition, incorrect contact data counts in the CPL even though it is useless.
Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS)
The ROAS indicates how big the profit of a campaign is after deducting the marketing costs. It can be calculated with the following formula:
Return on Advertising Spend in Euro (ROAS) = Sum of the value of all conversions in Euro / Sum of all advertising costs in Euro
ROAS is an important performance marketing KPI because it compares the revenue or value of the leads generated with the advertising costs. However, it is often difficult to measure because sales values are usually only recorded directly in online stores and can be attributed to a specific campaign.
Conclusion
If you want to be successful in performance marketing in the long term, you need to be able to reliably measure the effectiveness of the measures taken. This makes it easier to monitor and adjust them. Important KPIs such as Cost Per Action, Cost Per Order, Cost Per Lead, Cost Per Click and Cost Per View provide good support for this. The right selection of the appropriate KPIs allows targeted performance development of the marketing measures.
Would you like professional support with your performance marketing? We would be happy to support you with our many years of expertise. Contact us now!